What is Excoriation (Skin Picking) Disorder?

Excoriation Disorder, commonly known as skin-picking disorder, is a complex psychiatric condition characterized by the repetitive and compulsive picking of one’s skin, leading to noticeable tissue damage. This compulsive behavior goes beyond the occasional skin-picking that many individuals engage in and can have significant detrimental effects on one’s physical and mental well-being.
Introduction:
Excoriation Disorder emerges as a poignant challenge within the realm of mental health, captivating the attention of clinicians and researchers alike. This disorder transcends the ordinary, manifesting as an intricate interplay of psychological and physiological factors. Understanding its nuances is pivotal in fostering empathy and devising effective therapeutic interventions.
Definition:
Excoriation Disorder is defined by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) as an obsessive-compulsive and related disorder. Individuals afflicted by this condition experience an irresistible urge to pick at their skin, often causing lesions, scarring, and emotional distress. The compulsive nature of this behavior sets it apart, as affected individuals struggle to control or cease the repetitive act despite recognizing its adverse consequences.
Discovery:
The discovery of Excoriation Disorder traces its roots to the intersection of psychology and dermatology. Early observations recognized excessive skin picking as a distinctive pattern of behavior, prompting further exploration. Psychiatric pioneers delved into the intricate layers of this compulsion, unraveling its ties to underlying psychological distress. The disorder gained formal recognition with its inclusion in the DSM-5, marking a milestone in the acknowledgment of this unique mental health challenge.
History:
Historically, Excoriation Disorder has worn various labels, from dermatillomania to pathological skin picking. The journey of understanding this disorder is marked by a gradual evolution in nomenclature, reflecting advancements in psychiatric classification and comprehension. The historical narrative intertwines with societal perceptions of mental health, emphasizing the importance of destigmatization and informed discourse.
In conclusion, Excoriation Disorder is a testament to the intricate relationship between mental and physical well-being. Its exploration demands a holistic approach, acknowledging the psychological underpinnings and the tangible impact on an individual’s skin. As we delve into its depths, the evolving landscape of research and compassion beckons us to cultivate a nuanced understanding, fostering a supportive environment for those navigating the challenges posed by this rare and unique mental health condition.
Symptoms of Excoriation Disorder
Excoriation Disorder, also known as Dermatillomania, manifests through a myriad of distinctive symptoms, offering a profound insight into the complexities of this psychiatric condition. Recognizing these signs is imperative for early identification and intervention, paving the way for effective treatment. Here, we explore ten symptoms that characterize Excoriation Disorder, shedding light on its diverse clinical presentation.
Compulsive Skin Picking
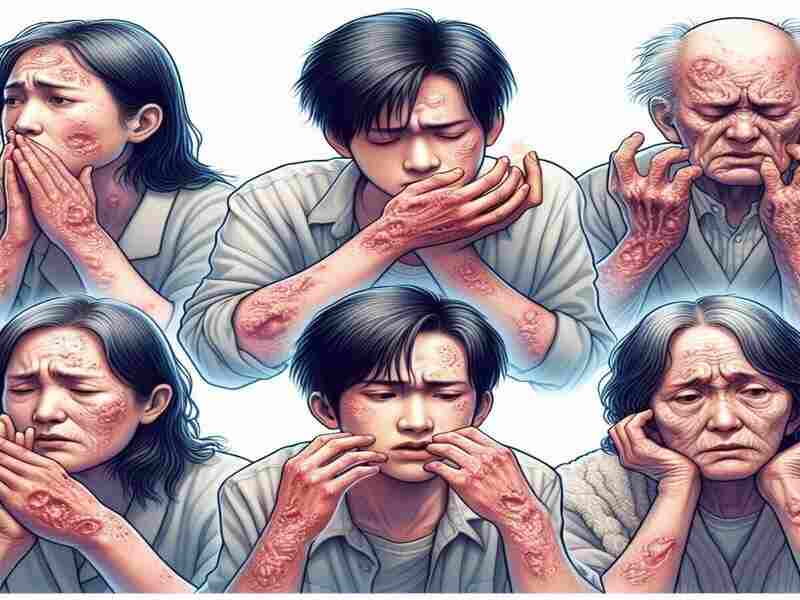
The hallmark symptom of Excoriation Disorder is the irresistible urge to pick at one’s skin repetitively. This compulsion extends beyond occasional grooming, becoming a pervasive behavior that individuals find challenging to control. The constant picking often leads to skin lesions, wounds, and scarring.
Preoccupation with Skin Imperfections
Individuals grappling with Excoriation Disorder frequently fixate on perceived imperfections in their skin. This preoccupation goes beyond normal skincare concerns, dominating their thoughts and triggering the compulsive need to address what others may consider minor blemishes.
Sense of Relief or Gratification
Engaging in skin picking provides a temporary sense of relief or gratification for those with Excoriation Disorder. This reinforces the compulsive behavior, as individuals seek solace in the act despite knowing potential physical and emotional repercussions.
Attempts to Stop Are Unsuccessful
Efforts to cease or reduce skin picking often prove futile for individuals with Excoriation Disorder. Despite recognizing the harmful consequences, the compulsive nature of the behavior overrides attempts to curb or control it.
Impact on Social and Occupational Functioning
Excoriation Disorder can significantly impair social and occupational functioning. The visible effects of constant skin picking may lead to self-consciousness, avoidance of social situations, and challenges in professional settings, contributing to a diminished quality of life.
Time-Consuming Rituals
The ritualistic nature of skin picking in Excoriation Disorder consumes considerable time. Individuals may find themselves engrossed in this behavior for extended periods, further highlighting the compulsive and disruptive nature of the disorder.
Skin Infections and Medical Complications
The repetitive nature of skin picking increases the risk of skin infections and other medical complications. Open wounds provide a gateway for infections, underscoring the importance of addressing Excoriation Disorder from both a mental health and medical perspective.
Feelings of Guilt and Shame

Those afflicted with Excoriation Disorder often grapple with intense feelings of guilt and shame surrounding their compulsive behavior. The awareness of its negative impact on physical appearance and the perceived lack of control contribute to a cycle of emotional distress.
Co-occurrence with Other Mental Health Conditions:
Excoriation Disorder frequently co-occurs with other mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Understanding these comorbidities is crucial for comprehensive treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Need for Professional Intervention:
Given the intricate nature of Excoriation Disorder, seeking professional help is paramount. Mental health professionals, including psychiatrists and therapists, play a pivotal role in diagnosis, treatment planning, and therapeutic interventions aimed at breaking the cycle of compulsive skin picking.
In essence, unraveling the tapestry of Excoriation Disorder involves a nuanced exploration of its multifaceted symptoms. Increased awareness and a compassionate approach to diagnosis and treatment are pivotal steps in supporting individuals affected by this challenging psychiatric condition.
Excoriation Disorder Causes
Excoriation Disorder, characterized by compulsive skin picking, is a complex mental health condition with origins rooted in a variety of factors. Understanding the potential causes of this disorder is essential for a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, treatment, and support. Here, we delve into ten reasons that shed light on the intricate tapestry of Excoriation Disorder.
Genetic Predisposition
Genetics plays a significant role in the development of Excoriation Disorder. Research suggests a hereditary component, indicating that individuals with a family history of obsessive-compulsive disorders or related conditions may be more predisposed to developing this compulsive skin-picking behavior.
Neurobiological Factors
Alterations in neurobiological processes contribute to the manifestation of Excoriation Disorder. Imbalances in neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, have been implicated, linking this disorder to the broader spectrum of obsessive-compulsive and related disorders.
Psychological Trauma
Experiences of psychological trauma, including but not limited to childhood abuse, neglect, or other adverse life events, can serve as catalysts for the development of Excoriation Disorder. The compulsion to pick at one’s skin may emerge as a maladaptive coping mechanism to manage the distress stemming from past traumas.
Stress and Anxiety
High levels of chronic stress and anxiety are recognized triggers for Excoriation Disorder. The compulsion to engage in skin picking may serve as a coping mechanism to alleviate heightened stress levels, creating a cycle where stress contributes to skin picking and vice versa.
Perfectionism and Body Dysmorphic Traits
Individuals with perfectionistic tendencies and body dysmorphic traits may be more susceptible to Excoriation Disorder. A fixation on perceived imperfections in the skin can drive the compulsive need to engage in skin-picking rituals to achieve an unattainable standard of perfection.
Cognitive Factors
Cognitive processes, such as intrusive thoughts and obsessive rumination, are integral to the development of Excoriation Disorder. The persistent fixation on skin imperfections and an inability to dismiss these thoughts contribute to the repetitive nature of skin picking.
Imitation and Social Learning
Social factors, including imitation and social learning, can influence the development of Excoriation Disorder. Individuals may observe or learn skin-picking behaviors from family members, peers, or through media exposure, leading to the adoption of this compulsive pattern.
Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors (BFRBs)
Excoriation Disorder falls under Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors (BFRBs), encompassing repetitive self-grooming behaviors. Individuals who already engage in BFRBs, such as hair pulling (trichotillomania), may be at an increased risk of developing Excoriation Disorder.
Comorbidity with Other Mental Health Conditions
Excoriation Disorder often coexists with other mental health conditions, such as anxiety disorders, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). The interplay of these conditions can exacerbate skin-picking behaviors, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive approach to address underlying complexities.
Environmental Factors
Environmental stressors, including challenging life circumstances, work pressures, or significant life changes, can contribute to the onset or exacerbation of Excoriation Disorder. Understanding the impact of the environment on an individual’s mental health is crucial for tailored treatment strategies.
In conclusion, the causes of Excoriation Disorder weave a complex narrative, highlighting the interplay of genetic, neurobiological, psychological, and environmental factors. Recognizing these diverse influences is instrumental in formulating personalized interventions that address the underlying dynamics of this unique and challenging mental health condition.
Impacts of Excoriation Disorder
Excoriation Disorder, with its relentless cycle of compulsive skin picking, extends its impact far beyond the visible surface. Understanding the profound effects on individuals afflicted by this condition is crucial for fostering empathy, offering support, and implementing effective interventions. Here, we explore ten impacts of Excoriation Disorder, delving into the intricate web it weaves in the lives of those grappling with this challenging mental health condition.
Physical Consequences
At its core, Excoriation Disorder leaves a tangible mark on the body. The constant skin picking results in open wounds, lesions, and scarring. Beyond the immediate visual impact, these physical consequences may lead to infections, chronic skin conditions, and long-term dermatological issues, further complicating an individual’s health.
Psychological Distress
The psychological toll of Excoriation Disorder is profound. Individuals experience heightened levels of anxiety, depression, and distress related to their compulsive skin-picking behavior. The constant preoccupation with perceived imperfections and the inability to control the compulsion contribute to a pervasive sense of emotional anguish.
Social Isolation

Excoriation Disorder often precipitates social isolation. Individuals may withdraw from social interactions due to embarrassment or shame associated with their visible skin lesions. The fear of judgment and the desire to conceal the effects of skin picking can lead to self-imposed isolation, exacerbating feelings of loneliness.
Occupational Challenges
The impact of Excoriation Disorder extends into the professional realm, affecting occupational functioning. Visible skin lesions may evoke judgment or misunderstanding from colleagues, potentially leading to workplace challenges. Concentration difficulties arising from the preoccupation with skin picking further compound these occupational hurdles.
Strained Relationships
Close relationships bear the brunt of the impact of Excoriation Disorder. Family members and friends may struggle to comprehend the compulsive nature of skin picking, leading to strained relationships. The emotional toll on both the individual with Excoriation Disorder and their loved ones can create barriers to understanding and support.
Time Consumption
Engaging in compulsive skin picking consumes a significant amount of time for individuals with Excoriation Disorder. This time investment interferes with daily activities and contributes to a cyclical pattern where the disorder becomes a pervasive and time-consuming aspect of everyday life.
Financial Implications
The financial impact of Excoriation Disorder may manifest in various ways. Individuals may incur expenses related to medical treatments for skin-related complications, Therapy, or dermatological interventions. Occupational challenges stemming from the disorder may also lead to financial strain.
Negative Body Image
Excoriation Disorder often gives rise to a distorted body image. Individuals may develop a heightened focus on perceived skin imperfections, fostering negative self-perception. This negative body image can further contribute to the cycle of compulsive skin-picking as individuals strive to attain an unrealistic standard of physical perfection.
Cycle of Shame and Guilt
A pervasive sense of shame and guilt characterizes the emotional impact of Excoriation Disorder. Individuals are acutely aware of the harm caused by their compulsive behavior, leading to a recurring cycle of shame and guilt. Breaking free from this cycle is a significant challenge, requiring tailored therapeutic interventions.
Impact on Quality of Life
Ultimately, the cumulative effect of Excoriation Disorder profoundly impacts an individual’s overall quality of life. The combination of physical, psychological, social, and occupational consequences creates a complex web that diminishes well-being. Addressing this impact necessitates a holistic approach that considers the multifaceted nature of the disorder.
In summary, the impacts of Excoriation Disorder reverberate across various aspects of an individual’s life, underscoring the need for comprehensive and compassionate support. Recognizing the intricacies of these impacts is a crucial step in guiding individuals toward effective interventions and fostering a greater understanding of this unique mental health challenge.
Diagnosis of Excoriation Disorder
Diagnosing Excoriation Disorder, also known as Dermatillomania, involves a meticulous exploration of behavioral patterns, psychological factors, and potential underlying causes. As a distinctive disorder within the realm of obsessive-compulsive and related disorders, accurate diagnosis is paramount for effective intervention and support. Here, we delve into the comprehensive process of diagnosing Excoriation Disorder, shedding light on the nuanced facets involved in identifying and understanding this complex mental health condition.
Clinical Assessment
The diagnostic journey begins with a thorough clinical assessment conducted by mental health professionals, including psychiatrists, psychologists, or licensed therapists. A comprehensive evaluation encompasses detailed discussions about the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and the impact of skin-picking behaviors on daily functioning.
Diagnostic Criteria (DSM-5)
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), serves as the primary diagnostic tool for mental health conditions, including Excoriation Disorder. To meet the criteria, the individual must engage in recurrent skin picking, resulting in skin lesions, and experience significant distress or impairment due to the behavior. The DSM-5 criteria provide a standardized framework for clinicians to identify and categorize the disorder.
Duration and Frequency
Diagnosis considers the duration and frequency of skin-picking behaviors. According to the DSM-5, symptoms should persist for a specified time, typically over at least 12 weeks, and occur with sufficient frequency to warrant clinical attention. This temporal perspective helps differentiate occasional skin picking from the persistent and compulsive nature indicative of Excoriation Disorder.
Rule Out Medical Causes
Before confirming an Excoriation Disorder diagnosis, clinicians may conduct medical assessments to rule out underlying dermatological or medical causes for skin lesions. Skin conditions, infections, or other physical ailments can present with similar symptoms, and a thorough examination ensures an accurate understanding of the individual’s health.
Severity Assessment
The severity of Excoriation Disorder is evaluated based on the extent of physical harm caused by skin picking and the impact on the individual’s overall well-being. Clinicians assess the severity to tailor treatment plans effectively, considering factors such as infections, scarring, and impairment in daily functioning.
Differential Diagnosis
Clinicians differentiate Excoriation Disorder from other mental health conditions with similar features, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or body dysmorphic disorder (BDD). A meticulous differential diagnosis is crucial for pinpointing the specific nature of the symptoms and guiding appropriate therapeutic approaches.
Collateral Information
Gathering collateral information from friends, family, or other significant individuals in the individual’s life provides valuable insights into the impact of Excoriation Disorder on relationships and daily functioning. This collaborative approach enhances diagnostic accuracy and ensures a holistic understanding of the individual’s experiences.
Functional Impairment
Assessing the functional impairment caused by Excoriation Disorder is integral to the diagnostic process. Clinicians explore how skin-picking behaviors affect an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, maintain relationships, and engage in occupational responsibilities. Understanding the functional impact guides the development of targeted interventions.
Psychological Assessments
Psychological assessments, such as standardized questionnaires or interviews, sometimes complement the diagnostic process. These assessments provide:
- Additional quantitative data.
- Aiding in the evaluation of symptom severity.
- Associated distress.
- The potential presence of comorbid mental health conditions.
Cultural Considerations
Diagnosing Excoriation Disorder involves cultural sensitivity, recognizing that cultural factors may influence the expression of symptoms and perceptions of distress. Clinicians must consider the individual’s cultural background to ensure a nuanced and inclusive approach to diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, diagnosing Excoriation Disorder is a multifaceted process that involves careful consideration of clinical criteria, duration and frequency of symptoms, collaboration with the individual and their support network, and a thorough assessment of functional impairment. A comprehensive approach that integrates medical and psychological perspectives ensures an accurate diagnosis and lays the foundation for tailored and effective interventions to support individuals grappling with this unique mental health challenge.
Treatments for Excoriation disorder
Addressing Excoriation Disorder, also known as Dermatillomania, requires a comprehensive and individualized approach to treatment. From psychotherapy to medication and self-help strategies, navigating the therapeutic landscape involves understanding the diverse array of interventions available. Here, we explore a broad spectrum of treatments for Excoriation Disorder, shedding light on the rare and unique methods employed to alleviate the challenges posed by this complex mental health condition.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-behavioral Therapy stands as a cornerstone in the treatment of Excoriation Disorder. CBT focuses on identifying and modifying maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors associated with skin picking. Through cognitive restructuring and behavior modification techniques, individuals learn coping strategies to manage triggers and reduce the compulsion to engage in skin picking.
Habit Reversal Training (HRT)
Habit Reversal Training is a specialized behavioral Therapy that targets repetitive behaviors like skin picking. This intervention involves increasing awareness of the habit, identifying triggers, and implementing competing responses to replace the skin-picking behavior. HRT empowers individuals to interrupt the automatic sequence of skin picking and develop healthier alternatives.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy centers on mindfulness and acceptance of distressing thoughts and feelings. ACT helps individuals with Excoriation Disorder build psychological flexibility, allowing them to accept urges to pick without acting on them impulsively. This therapeutic approach emphasizes aligning actions with personal values to foster meaningful behavior change.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, Dialectical Behavior Therapy incorporates skills training to address emotional dysregulation and impulsive behaviors. In the context of Excoriation Disorder, DBT equips individuals with distress tolerance and emotion regulation skills, providing alternative coping mechanisms to manage stressors without resorting to skin picking.
Medication
Certain medications may be prescribed to complement psychotherapeutic interventions for Excoriation Disorder. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), commonly used to treat anxiety and depression, have shown efficacy in some cases. Naltrexone, an opioid receptor antagonist, is another medication under investigation for its potential to reduce compulsive behaviors.
Mindfulness-Based Interventions
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and mindful awareness, are vital in managing Excoriation Disorder. These interventions cultivate present-moment awareness, helping individuals observe and detach from the urge to pick at their skin. Mindfulness-based strategies enhance self-regulation and promote a non-judgmental attitude toward thoughts and sensations.
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
ERP, a component of cognitive-behavioral Therapy, involves exposing individuals to situations that trigger skin picking and preventing the associated response. By gradually confronting and resisting the urge to pick, individuals learn to tolerate discomfort and reduce the reinforcing effects of the compulsion.
Group Therapy

Group therapy provides a supportive environment where individuals with Excoriation Disorder can share experiences, gain insights, and receive encouragement from peers facing similar challenges. Group sessions often incorporate elements of cognitive-behavioral Therapy and allow for mutual support and accountability.
Psychodynamic Psychotherapy
Psychodynamic psychotherapy explores the underlying emotional and relational aspects contributing to Excoriation Disorder. By delving into unconscious processes and unresolved conflicts, this therapeutic approach aims to uncover the roots of compulsive behavior, fostering self-awareness and promoting lasting change.
Self-Help Strategies
Empowering individuals to participate in their treatment actively, self-help strategies play a crucial role in managing Excoriation Disorder. This may include journaling, creating awareness logs to track triggers, and practicing self-compassion. Self-help resources, such as books and online communities, offer additional support and guidance.
In conclusion, the treatment landscape for Excoriation Disorder is rich and diverse, reflecting the multifaceted nature of this mental health condition. A combination of psychotherapeutic modalities, medication, and self-help strategies provides a holistic approach to addressing the intricate challenges posed by skin-picking behaviors. Tailoring interventions to the individual’s unique needs ensures a personalized and effective path toward recovery, fostering a journey of healing and empowerment.
20 Famous People with Excoriation Disorder
Excoriation Disorder, marked by compulsive skin picking, is a mental health challenge that transcends societal boundaries, impacting individuals from all walks of life. While the condition is often discreet, some well-known figures have shared their struggles with Excoriation Disorder, contributing to a broader understanding and destigmatization of mental health issues. Here, we highlight 20 confirmed famous people who have publicly acknowledged their experiences with Excoriation Disorder, shedding light on the human aspect of this unique mental health condition.
Adele
The Grammy-winning singer Adele has openly discussed her battle with Excoriation Disorder, emphasizing the importance of mental health awareness in the public eye.
Justin Timberlake
Renowned musician and actor Justin Timberlake has shared his journey of coping with Excoriation Disorder, highlighting the need for compassion and understanding surrounding mental health.
Emma Stone
Academy Award-winning actress Emma Stone has spoken candidly about her struggles with anxiety, including Excoriation Disorder, promoting conversations about mental health in the entertainment industry.
Ed Sheeran
Singer-songwriter Ed Sheeran has revealed his experiences with Excoriation Disorder, contributing to the dialogue on mental health within the music community.
Zayn Malik
Former One Direction member Zayn Malik has openly discussed his battle with anxiety and Excoriation Disorder, encouraging fans to prioritize their mental well-being.
Chrissy Teigen
Model and author Chrissy Teigen has shared her journey with Excoriation Disorder on social media, fostering an open dialogue about mental health and self-care.
Halsey
Singer-songwriter Halsey has been vocal about her experiences with mental health challenges, including Excoriation Disorder, advocating for increased awareness and understanding.
John Green
Author John Green, known for works like “The Fault in Our Stars,” has spoken about his struggles with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), a condition often associated with Excoriation Disorder.
Selena Gomez
Actress and singer Selena Gomez has been candid about her mental health journey, discussing anxiety and related conditions, including Excoriation Disorder.
Michael Phelps
Olympic swimmer Michael Phelps has shared his battles with anxiety and depression, shedding light on mental health issues in the world of professional sports.
Demi Lovato
Pop star Demi Lovato has been a vocal advocate for mental health awareness, openly discussing her struggles with conditions such as Excoriation Disorder.
Howie Mandel
Comedian and television personality Howie Mandel has been public about his experiences with obsessive-compulsive disorder, contributing to the conversation around mental health in the entertainment industry.
Nadiya Hussain
Celebrity chef and author Nadiya Hussain has spoken about her journey with anxiety, providing a relatable perspective on mental health in the culinary world.
Carrie Fisher
The late Carrie Fisher, beloved for her iconic role as Princess Leia in “Star Wars,” was candid about her experiences with mental health, including Excoriation Disorder.
Bo Burnham
Comedian and filmmaker Bo Burnham has incorporated themes of mental health into his work, discussing his struggles with conditions like Excoriation Disorder.
Katy Perry
Pop sensation Katy Perry has shared her experiences with mental health challenges, including moments of anxiety and stress, contributing to a more open dialogue in the music industry.
Adam Levine
Maroon 5 frontman Adam Levine has acknowledged his journey with anxiety and Excoriation Disorder, adding his voice to the conversation on mental health in the music world.
Jameela Jamil
Actress and activist Jameela Jamil has been outspoken about her struggles with mental health, emphasizing the importance of self-acceptance and breaking societal stigmas.
Howie Dorough
Backstreet Boys member Howie Dorough has discussed his experiences with obsessive-compulsive disorder, providing insight into the challenges faced by individuals with conditions like Excoriation Disorder.
Mara Wilson
Former child actress Mara Wilson, known for her roles in films like “Matilda,” has shared her experiences with mental health, fostering understanding and empathy for those navigating conditions like Excoriation Disorder.
In highlighting these famous individuals who have spoken openly about their struggles with Excoriation Disorder, we emphasize that mental health knows no boundaries. Their courage in sharing their stories contributes to reducing stigma and encouraging others to seek support and understanding on their mental health journeys.


Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!